Difference between Cord Blood and Blood Stem Cell Transplants
There are three main sources of hematopoietic(blood-forming) blood stem cells for patients who need transplantation – Bone Marrow, PBSC and Umbilical Cord Blood. All these methods are used to replace unhealthy cells with healthy ones for patients suffering from different forms of blood cancers.
INTRODUCTION
There are three main sources of hematopoietic(blood-forming) blood stem cells for patients who need transplantation – Bone Marrow, PBSC and Umbilical Cord Blood.
All these methods are used to replace unhealthy cells with healthy ones for patients suffering from Leukemia, Thalassemia, Aplastic Anemia and other forms of blood cancers.
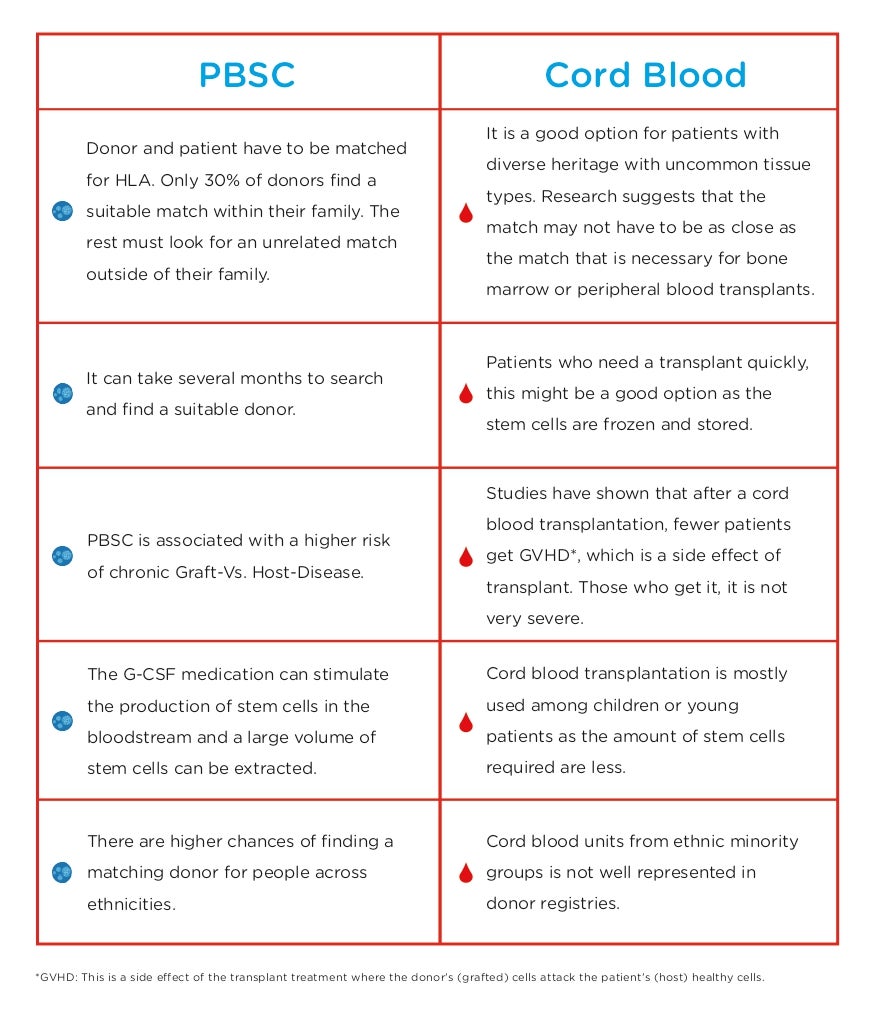
The availability of HLA-matched related or unrelated donors is the primary consideration in the selection of a donor, but donor health or donation preferences may restrict what products will be available to the recipient. The patient's physician may select a stem cell source based on the expected transplant outcomes.
WHAT IS CORD BLOOD?
Cord blood is collected from an umbilical cord or the placenta after the birth of a child. The placenta/cord blood contains many blood-forming stem cells. It is collected, tested, frozen, and stored in a cord blood bank for future use.
Even though cord blood has been used for decades, it has only recently been gaining more popularity for the treatment of certain blood cancers and blood disorders. It is used for young and adult patients, but mostly for treating children. The reason being a cord blood unit has a limited number of stem cells. Younger patients, especially children, will receive enough blood stem cells from one cord blood unit. Adults generally require a larger quantity of stem cells.
WHAT IS PBSC?
PBSC(Peripheral Blood stem Cell) is the most common source of stem cell for transplants. PBSC are blood-forming cells that are released from the bone marrow into the bloodstream. To obtain a higher number of stem cells, a donor is administered G-CSF for a few days before the donation, which stimulates the production of stem cells and is released into the bloodstream. The stem cells are then collected from the donor’s arm via an Apheresis machine and the rest of the blood is transferred back to the donor.
CONCLUSION
Unlike the rest of the world, where Cord Blood units are being used for transplants in treating blood cancers and blood disorders. In India, Cord Blood Banks only provide this facility for families who wish to preserve the cord blood in a private bank. Thus, cord blood units can be retrieved only by the family. There is no public cord blood bank in India and therefore physicians cannot request a cord blood unit from an unrelated donor.


